Pandas และ PySpark เป็นเครื่องมือที่ใช้สำหรับการจัดการและวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลใน Python โดย Pandas เป็นไลบรารียอดนิยมที่ใช้สำหรับการทำงานกับชุดข้อมูลขนาดเล็ก ถึงขนาดกลาง ในหน่วยความจำบนเครื่องเดียว (single-node) ซึ่งมีฟังก์ชันหลากหลายสำหรับการจัดการและวิเคราะห์ข้อมูล ในทางตรงกันข้าม PySpark ซึ่งสร้างขึ้นบน Apache Spark ได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อการประมวลผลแบบกระจาย (distributed computing) ทำให้สามารถประมวลผลชุดข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่ได้บนหลายเครื่องใน cluster เดียว
Pandas คืออะไร
Pandas เป็นหนึ่งใน library แบบ open-source ที่ถูกใช้งานมากที่สุดใน Python สำหรับข้อมูลที่มีโครงสร้างแบบตารางเพื่อการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลได้หลากหลาย เช่น การกรองข้อมูล การรวมข้อมูล การแปลงข้อมูล รวมถึงการทำความสะอาดและเตรียมข้อมูล จนไปถึงการทำ Machine Learning และอื่น ๆ อีกมากมาย โดยสามารถอ่านไฟล์ได้ในหลายรูปแบบ เช่น CSV, JSON, SQL และรูปแบบอื่นๆ จากนั้นจะสร้างข้อมูลในรูปแบบ DataFrame ซึ่งเป็นวัตถุที่มีโครงสร้างประกอบด้วยแถวและคอลัมน์ (คล้ายกับตาราง SQL)
ตัวอย่างการใช้งาน Pandas DataFrame
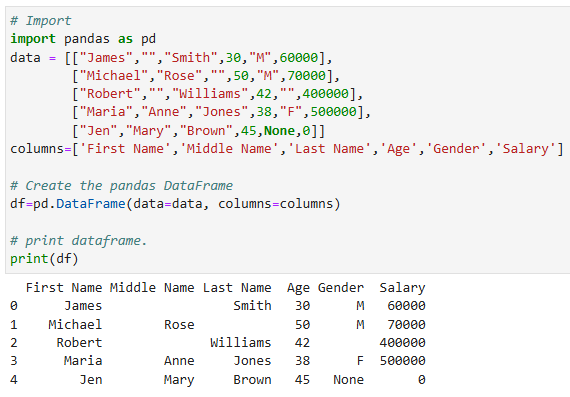
เริ่มต้นใช้งาน Pandas library โดยการ import library และสร้าง DataFrame ด้วยฟังก์ชัน pd.DataFrame โดยได้ผลลัพธ์ออกมาเป็นตารางที่มี index เริ่มที่ index 0
ตัวอย่าง Pandas Transformations
ฟังก์ชันต่าง ๆ ในกระบวนการแปลงของ Pandas DataFrame ซึ่งรวมถึงฟังก์ชันทางคณิตศาสตร์ หรือฟังก์ชันทางสถิติ ที่สามารถเลือกทำได้ในทั้ง DataFrame หรือเลือกทำในแต่ละ column เป็นตัวช่วยให้จัดการและวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลยืดหยุ่นมากขึ้น ตัวอย่างเช่น
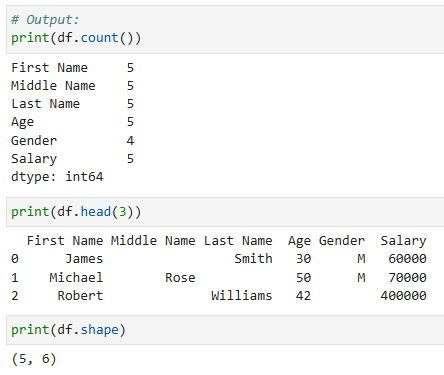
- df.count() จะให้ค่ากลับมาเป็นการนับจำนวนข้อมูลที่ไม่เป็น Null ในแต่ละ column
- df.corr() จะให้ค่ากลับมาเป็นค่า correlation ระหว่าง column ใน data frame
- df.head(n) จะให้ค่ากลับมาเป็นจำนวน n แถวแรก
- df.max() จะให้ค่ากลับมาเป็นค่าสูงสุดของแต่ละ column
- df.shape จะให้ค่ากลับมาเป็น tuple (n,m) โดยที่ n คือจำนวนแถว และ m คือจำนวน column
PySpark คืออะไร
PySpark เป็น API ของ Python สำหรับ Apache Spark ซึ่งเป็นกรอบการประมวลผลแบบกระจาย (distributed computing) ที่ออกแบบมาสำหรับการประมวลผลชุดข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่ใน cluster ของเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์ โดยที่ PySpark ช่วยให้การประมวลผลและวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลแบบขนานเป็นไปได้โดยการกระจายการคำนวณไปยังหลาย node ใน cluster ซึ่งทำให้มีความสามารถในการขยายขนาด (scalability) และมีประสิทธิภาพสูงสำหรับงานวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่ ซึ่ง PySpark มี API DataFrame ที่มีลักษณะคล้ายกับ Pandas ทำให้ผู้ใช้งานสามารถทำการจัดการข้อมูลได้คล้ายกัน แต่บนชุดข้อมูลที่กระจายกันอยู่ (Distributed Datasets)
ตัวอย่างการใช้งาน PySpark DataFrame
PySpark DataFrame เป็นวัตถุที่ไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงค่าได้ (immutable) ซึ่งหมายความว่าไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้เมื่อสร้างขึ้นแล้ว มีความสามารถในการทนต่อข้อผิดพลาด (fault-tolerant) และการทำ Transformations จะเป็น Lazy evaluation ซึ่งหมายความว่าจะไม่ถูกดำเนินการจนกว่าจะมีการเรียกใช้ Actions เช่น count(), collect(), show() เป็นต้น ซึ่ง PySpark DataFrames จะถูกกระจายอยู่ใน cluster (ซึ่งหมายถึงข้อมูลใน PySpark DataFrames จะถูกจัดเก็บในเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์ต่าง ๆ ใน cluster เดียว) และการดำเนินการใด ๆ ใน PySpark จะถูกดำเนินการแบบขนานบนเครื่องทั้งหมดใน cluster
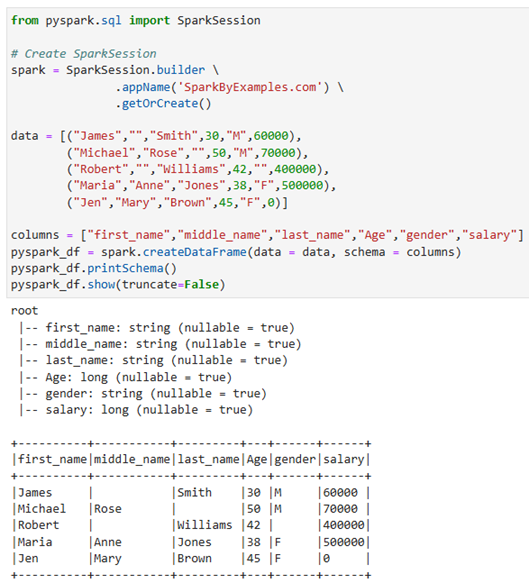
เริ่มต้นโดยการ import และสร้าง SparkSession และสร้าง DataFrame ด้วย spark.createDataFrame โดยได้ผลลัพธ์ออกมาเป็นตารางที่ไม่มี index และเมื่อต้องการแสดงตาราง ให้ใช้ฟังก์ชัน show()
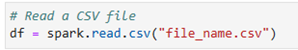
และสามารถอ่านไฟล์ได้ เช่น การอ่าน csv file ด้วยฟังก์ชัน spark.read.csv
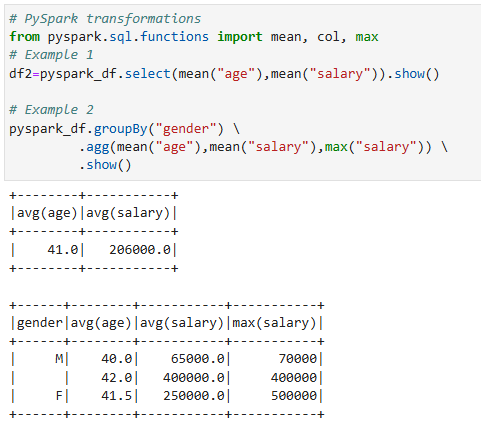
ตัวอย่าง PySpark Transformations
การทำ Transformations ใน PySpark มีลักษณะเป็นแบบ Lazy evaluation ซึ่งหมายความว่าจะไม่ถูกดำเนินการจนกว่าจะมีการเรียกใช้ Actions ตัวอย่างการแปลงใน PySpark มีดังนี้
- select() จะใช้เพื่อเลือก column ที่สนใจใน DataFrame และสามารถใช้ฟังก์ชันการคำนวณเพื่อสร้าง column ใหม่
- filter() ใช้เพื่อเลือกแถวที่สอดคล้องกับเงื่อนไขที่กำหนด
- groupBy() ใช้เพื่อจัดกลุ่มตามข้อมูลใน column ที่สนใจ และสามารถใช้ฟังก์ชันการคำนวณเพื่อสร้าง column ใหม่
- dropDuplicates() ใช้เพื่อลบข้อมูลแถวที่ซ้ำกับแถวอื่นใน DataFrame
- join() ใช้สำหรับประสานข้อมูล 2 DataFrames ซึ่งมี column เดียวกัน หรือเลือก column ที่ต้องการเป็นตัวประสาน
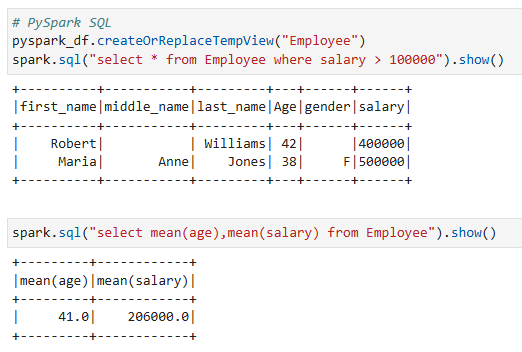
ตัวอย่างการใช้งาน PySpark SQL
PySpark รองรับการใช้คำสั่ง SQL เพื่อดำเนินการแปลงข้อมูล (Transformation) ซึ่งที่ต้องทำคือการสร้างตาราง (Table) หรือมุมมอง (View) จาก PySpark DataFrame
ตัวอย่าง
Note !!
- สามารถสร้าง PySpark DataFrame จาก Pandas DataFrame โดยใช้ฟังก์ชัน spark.createDataFrame(df)
- สามารถสร้าง Pandas DataFrame จาก PySpark DataFrame โดยใช้ฟังก์ชัน pyspark_df.toPandas()
วิธีการตัดสินใจเลือกระหว่างใช้ Pandas หรือ PySpark
การตัดสินใจเลือกระหว่าง Pandas หรือ PySpark มีหลายองค์ประกอบในการตัดสินใจ ไม่ว่าจะเป็น ขนาดของข้อมูล ทรัพยากรในการประมวลผลที่มีอยู่ และความต้องการเฉพาะของงานวิเคราะห์ข้อมูล
- ขนาดของข้อมูล
- ใช้ Pandas สำหรับชุดข้อมูลขนาดเล็กถึงขนาดกลางที่สามารถจัดเก็บในหน่วยความจำและต้องการในการจัดการและวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลแบบรวดเร็วภายในหน่วยความจำนั้น ๆ
- ใช้ PySpark สำหรับชุดข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่ที่เกินขีดความสามารถของหน่วยความจำในเครื่องเดียว และต้องการความสามารถในการประมวลผลแบบกระจาย (distributed computing) เพื่อดำเนินการประมวลผลข้อมูลแบบขนาน
- ทรัพยากรการประมวลผล
- หากทรัพยากรในการประมวลผลมีอย่างจำกัดหรือทำงานใน Environment เครื่องเดียว การเลือกใช้ Pandas อาจเหมาะสมกว่าเนื่องจากความสามารถในการประมวลผลภายในหน่วยความจำเดียว
- สำหรับ Environment ในการประมวลผลแบบกระจาย (distributed computing) ที่สามารถเข้าถึง cluster ของเครื่องได้หลายเครื่องนั้น PySpark ช่วยให้การประมวลผลสามารถขยายขนาดและทำงานแบบขนานได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ สำหรับการจัดการชุดข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่มากใน cluster ที่กระจาย
- ประสิทธิภาพ
- Pandas ทำงานได้ดีสำหรับชุดข้อมูลขนาดเล็กถึงขนาดกลาง แต่ถ้าข้อมูลมีขนาดใหญ่ อาจจะทำให้ประสบปัญหาเรื่องข้อจำกัดของหน่วยความจำได้
- PySpark จะเหมาะในการประมวลผลชุดข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่ที่ถูกแบ่งออกจากส่วนย่อย ๆ ที่กระจายไปตาม node ต่าง ๆ ใน cluster ซึ่งให้จะเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพในการขยายและการประมวลผลข้อมูลแบบขนาน (Parallelism)
- ระบบนิเวศและการผสานรวม
- ระบบนิเวศของ Pandas เป็นที่ยอมรับ โดยมีการสนับสนุนอย่างมากในส่วนของเครื่องมือในการจัดการข้อมูล การแสดงผล และการวิเคราะห์ ทำให้เหมาะสำหรับงานวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลที่หลากหลาย
- PySpark จะใช้ร่วมกับระบบนิเวศของ Apache Spark ซึ่งเป็นแหล่งข้อมูลต่าง ๆ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นไลบรารีการเรียนรู้ของเครื่อง (machine learning) หรือความสามารถในการประมวลผลข้อมูลที่ไหลเข้ามาอย่างต่อเนื่อง (real-time data)
References
- https://sparkbyexamples.com/pyspark/pandas-vs-pyspark-dataframe-with-examples/
- https://medium.com/geekculture/pandas-vs-pyspark-fe110c266e5c
บทความโดย ดร.ภิรมย์มาส เตชิตณัฏฐ์ศรุต
ตรวจทานและปรับปรุงโดย ดร.ขวัญศิริ ศิริมังคลา
Senior Data Scientist
Big Data institute (BDI)
- This author does not have any more posts.